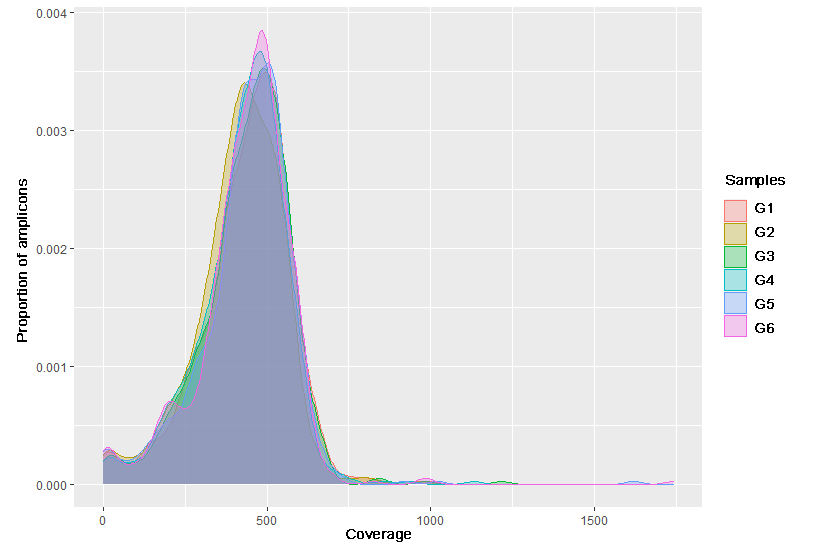
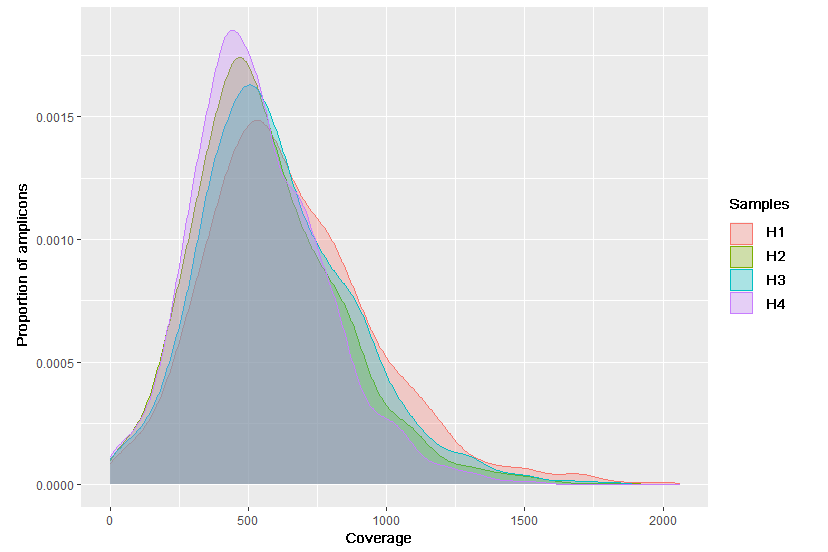
Typically, hotspots are understood as clinically significant variants, in a broader sense - any variants of interest. For design we recommend taking account of hotspots to understand if they are covered by panel design; to make sure that they are not on the edges of the amplicons (sequencing errors sometimes occur at the edge positions); to determine whether hotspots fall into regions difficult for sequencing (homopolymers, repeats, regions with a high degree of homology). If hotspots located into such regions, various primer modifications can be added to the design to improve genotyping.